FEP
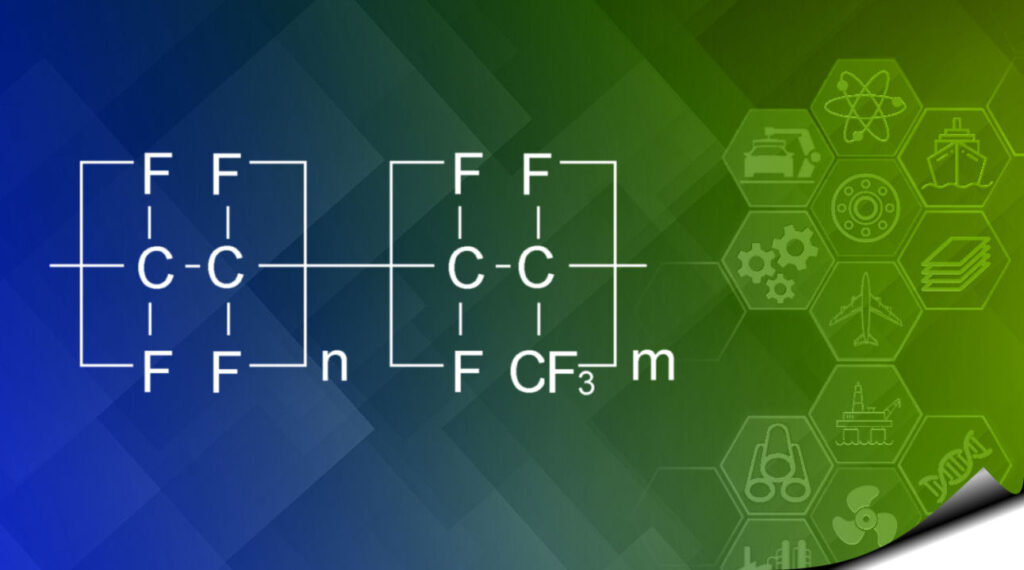
- Similarities to PTFE
- Pure carbon fluorine structure – fully fluorinated
- High flexibility
- Specified as alternative to PTFE for given applications
- Excellent corrosion resistance
Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP)
FEP has excellent corrosion resistance, FEP is the only other readily available fluoropolymer that can match PTFE’s own resistance to caustic agents, as it is a pure carbon-fluorine structure and fully fluorinated.
Thermally, FEP stands out from PTFE and PFA by having a melting point of 260°C (500°F), around forty degrees lower than PFA and lower again than PTFE.
Electrically, PTFE, FEP and PFA have identical dielectric constants, but FEP’s dielectric strength is only surpassed by PFA. However, while PFA has a similar dissipation factor to PTFE, FEP’s dissipation is around six times that of PFA and EFTE (making it a more non-linear conductor of electrostatic fields).
Mechanically, FEP is slightly more flexible than PTFE. Perhaps surprisingly, it does not withstand repetitive folding as well as PTFE. It also features a higher coefficient of dynamic friction, is softer and has a slightly lower tensile strength than PTFE and PFA.
A noteworthy property of FEP is that it is vastly superior to PTFE in some coating applications involving exposure to detergents.
Like PTFE, FEP is mainly used for wiring, e.g. hookup wire, coaxial cable, wiring for computer wires and technical gear.
In manufacturing high-quality composite parts, such as in the aerospace industry, FEP film can be used to protect moulds during the curing process. In such applications, the film is called “release film” and is intended to prevent the curing adhesive polymer (e.g. the epoxy in a carbon fibre/epoxy composite laminate) from bonding to the metal tooling. Being able to maintain chemical composure in extreme temperatures and resist damage from chemical fuels further makes FEP a suitable choice in the industry.
Semi-finished products like pipes, round bars, and sheets for lining containment vessels, gas scrubbers, and tanks are being used in diverse applications in the chemical-processing industry to safely contain and distribute highly-aggressive chemical compounds.
Due to its flexibility, extreme resistance to chemical attack and optical transparency, this material, along with PFA is routinely used for plastic labware and tubing that involves critical or highly corrosive processes.
It is also used in UV cured resin 3D printing. Due to the aforementioned properties of high optical transparency and low friction, it is ideally suited for use on the bottom of the resin reservoir (opposite the build plate). This allows for the ultraviolet light to penetrate into the resin, then after the layer has hardened, the build plate can move away pulling the hardened resin away from the FEP film.
The plastic is useful as a sample holder material in microscopy applications as its refractive index is close to that of water at visible wavelengths (FEP: 1.344, water: 1.335). This minimizes the blur due to optical aberrations when the light traverses the sample container.
"Excellence afforded"
Ultra high performance polymers – delivered globally
